
CONCRETE STRENGTH MONITORING USING APPLICATIONS OF IOT
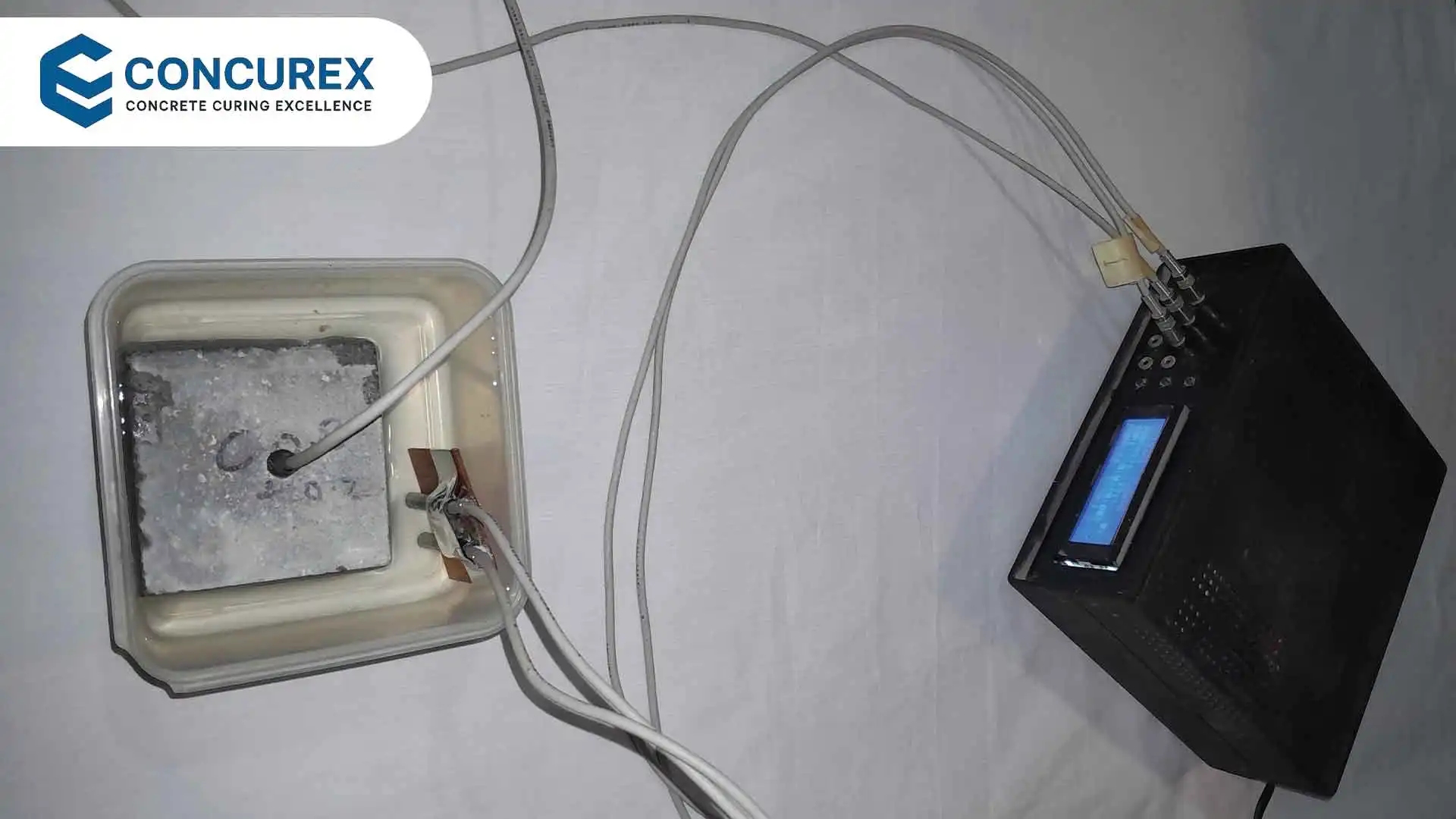
This paper explores the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technology for monitoring concrete strength during the curing process. By employing a thermocouple temperature sensor,

This paper explores the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technology for monitoring concrete strength during the curing process. By employing a thermocouple temperature sensor,

This paper investigates very early‑age hydration monitoring of self‑compacting concrete (SCC) containing fly ash replacement ratios (0%, 15%, 30%, 45%, 60%) using embedded piezoelectric (PZT)

This research develops an IoT‑enabled system by embedding temperature sensors within concrete for real‑time tracking of internal temperature‑time history, then using established maturity models (based
This paper presents a novel method for monitoring the strength development of early‑age concrete using embedded smart aggregates (SAs) that leverage electromechanical impedance (EMI) sensing
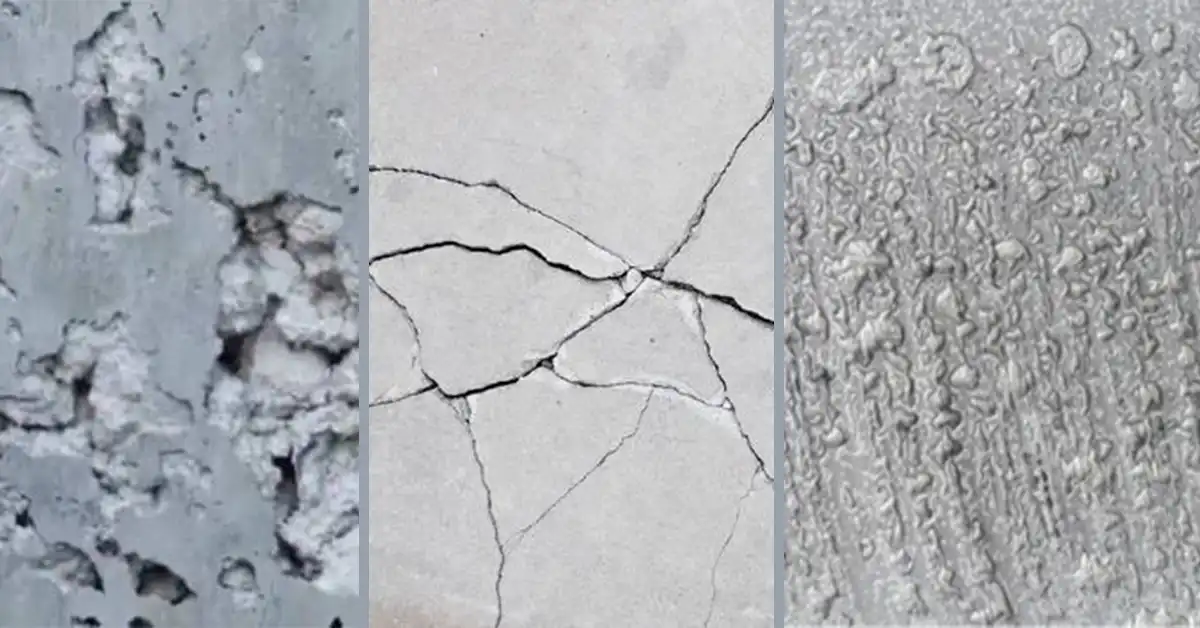

Curing is often underestimated, yet it’s one of the most critical factors influencing the strength, durability, and long-term performance of concrete. Improper curing can lead

The combination of IoT and AI technologies for improving concrete curing processes, has led to significant advancement in the construction industries to improve quality control

What makes concrete the unrivaled beast of the construction industry? What merges this titan to the backbone of skyscrapers, bridges, tunnels, and civil infrastructures? This

This paper explores the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technology for monitoring concrete strength during the curing process. By employing a thermocouple temperature sensor,

This paper investigates very early‑age hydration monitoring of self‑compacting concrete (SCC) containing fly ash replacement ratios (0%, 15%, 30%, 45%, 60%) using embedded piezoelectric (PZT)

This research develops an IoT‑enabled system by embedding temperature sensors within concrete for real‑time tracking of internal temperature‑time history, then using established maturity models (based

This paper presents a novel method for monitoring the strength development of early‑age concrete using embedded smart aggregates (SAs) that leverage electromechanical impedance (EMI) sensing

Curing is often underestimated, yet it’s one of the most critical factors influencing the strength, durability, and long-term performance of concrete. Improper curing can lead
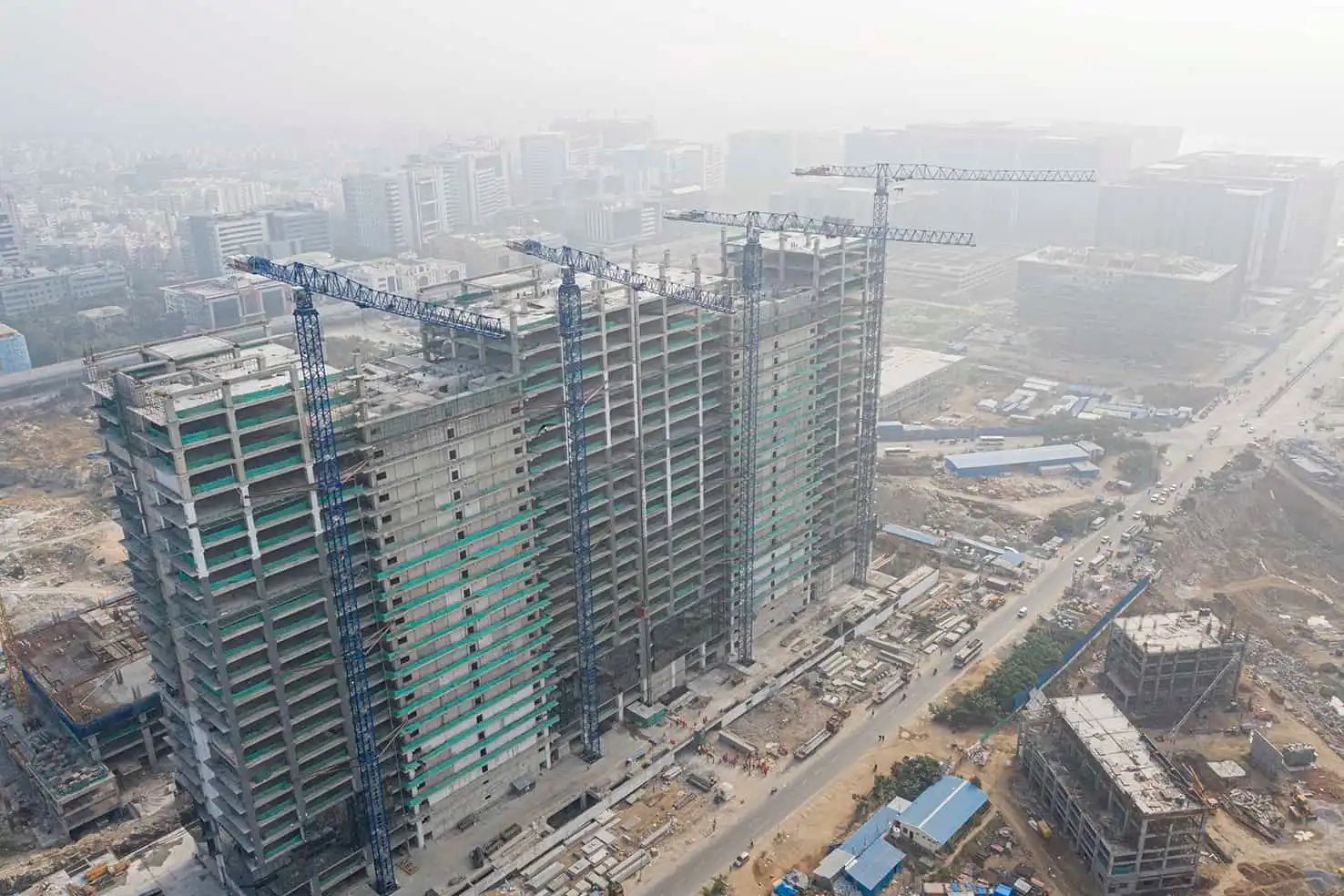

Precast concrete has been a game changer in the construction industry due to its versatility, speed, and cost-effectiveness. It allows for the creation of complex
Sign up for more information

This paper explores the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technology for monitoring concrete strength during the curing process. By employing a thermocouple temperature sensor,

This paper investigates very early‑age hydration monitoring of self‑compacting concrete (SCC) containing fly ash replacement ratios (0%, 15%, 30%, 45%, 60%) using embedded piezoelectric (PZT)

This research develops an IoT‑enabled system by embedding temperature sensors within concrete for real‑time tracking of internal temperature‑time history, then using established maturity models (based

This paper presents a novel method for monitoring the strength development of early‑age concrete using embedded smart aggregates (SAs) that leverage electromechanical impedance (EMI) sensing

Curing is often underestimated, yet it’s one of the most critical factors influencing the strength, durability, and long-term performance of concrete. Improper curing can lead

Precast concrete has been a game changer in the construction industry due to its versatility, speed, and cost-effectiveness. It allows for the creation of complex